Overview
Generally, the batch system where the batch window is severe (time available for batch processing) is designed
to reduce overall processing time as much as possible by operating multiple jobs in parallel (hereafter referred to as parallel processing).
However, it may happen that processing time does not fit in the batch window due to large size of 1 processing job.
In this case, a method to reduce processing time by dividing the processing data of a job and performing multiple processing (hereafter referred to as multiple processing) can be used.
Although parallel processing and multiple processing can be handled with the same significance, the definitions are given here as below.
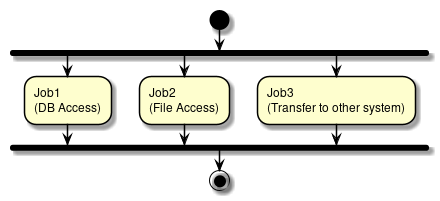
- Parallel processing
-
Execute multiple different jobs at the same time.
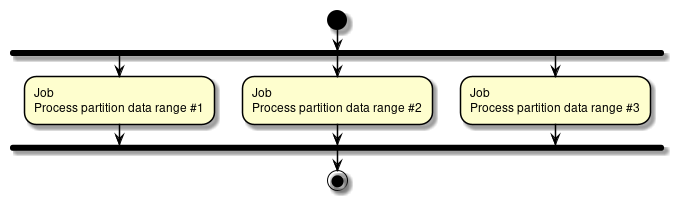
- Multiple processing
-
Divide the processing target of 1 job and execute simultaneously.
A method to use job scheduler and a method to use TERASOLUNA Batch 5.x are used for both parallel processing and multiple processing.
Note that, parallel processing and multiple processing in TERASOLUNA Batch 5.x is established
on Flow control.
| Implementation method | Parallel processing | Multiple processing |
|---|---|---|
Job scheduler |
It is defined to enable execution of multiple different jobs without dependencies to run at the same time. |
It is defined to execute multiple identical jobs in different data scopes. Pass information to narrow down data to be processed by each job argument, to each job. |
TERASOLUNA Batch 5.x |
Parallel Step (Parallel processing) |
Partitioning Step (Multiple processing) |
- When job scheduler is used
-
Since 1 process is allocated to 1 job, it is activated by multiple processes. Hence, designing and implementing one job is not very difficult.
However, since multiple processes are started, the load on machine resources increase when number of synchronous executions increase.
Hence, when the number of synchronous executions is 3 or 4, a job scheduler may be used.
Of course, this number is not absolute. It would like you to used as a guide as it depends on execution environment or job implementation. - When TERASOLUNA Batch 5.x is used
-
Since each step is assigned to a thread, it is operated as 1 process with multiple threads. Hence, the difficulty level for design and implementation of 1 job is higher than while using a job scheduler.
However, since the process is implemented by multiple threads, the load on machine resources will not be as high as the time when job scheduler is used even when the number of synchronous executions show an increase. Hence, when number of synchronous executions is large (5 or more than 5), TERASOLUNA Batch 5.x may be used.
Of course, this number is not absolute. It would like you to used as a guide as it depends on execution environment and system characteristics.
|
One of the parallel processing methods that can be executed in Spring Batch is
|
|
When data is to be updated to 1 database by parallel processing and multiple processing, resource conflict and deadlock are likely to occur. Potential conflicts should be eliminated from the job design stage. Distributed processing for multiple processes and multiple housings is included in Spring Batch as a function. However, since the failure design becomes difficult for TERASOLUNA Batch 5.x, it should not be used. |
The usage method of this function is same in the chunk model as well as tasklet model.
Parallel processing and multiple processing by job scheduler
Parallel processing and multiple processing using a job scheduler is explained here.
For job registration and schedule setting, refer the manual of the job scheduler to be used.
Parallel processing of jobs using job scheduler
The processes to be executed in parallel are registered as jobs and schedules are set so that each job starts on the time. Each job can be registered as a different process.
Multiple processing of jobs using job scheduler
Processes to be subjected to multiple processing are registered multiple times and extraction scope of target data is specified by parameters. Further, the schedule is set to enable the respective jobs at the same time. Although each job is in the same process, data range to be processed must be independent.
How to use
A method to perform parallel processing and multiple processing in TERASOLUNA Batch 5.x is explained.
Parallel Step (Parallel processing)
A method of Parallel Step (parallel processing) is explained.
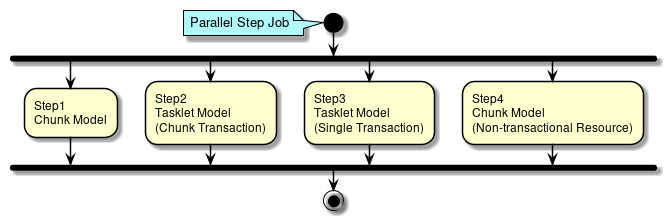
Separate processes can be defined for each step and can be executed in parallel. A thread is allocated for each step.
How to define Parallel Step is shown below using schematic diagram of Parallel Step.
<!-- Task Executor -->
<!-- (1) -->
<task:executor id="parallelTaskExecutor" pool-size="10" queue-capacity="200"/>
<!-- Job Definition -->
<!-- (2) -->
<batch:job id="parallelStepJob" job-repository="jobRepository">
<batch:split id="parallelStepJob.split" task-executor="parallelTaskExecutor">
<batch:flow> <!-- (3) -->
<batch:step id="parallelStepJob.step.chunk.db">
<!-- (4) -->
<batch:tasklet transaction-manager="jobTransactionManager">
<batch:chunk reader="fileReader" writer="databaseWriter"
commit-interval="100"/>
</batch:tasklet>
</batch:step>
</batch:flow>
<batch:flow> <!-- (3) -->
<batch:step id="parallelStepJob.step.tasklet.chunk">
<!-- (5) -->
<batch:tasklet transaction-manager="jobTransactionManager"
ref="chunkTransactionTasklet"/>
</batch:step>
</batch:flow>
<batch:flow> <!-- (3) -->
<batch:step id="parallelStepJob.step.tasklet.single">
<!-- (6) -->
<batch:tasklet transaction-manager="jobTransactionManager"
ref="singleTransactionTasklet"/>
</batch:step>
</batch:flow>
<batch:flow> <!-- (3) -->
<batch:step id="parallelStepJob.step.chunk.file">
<batch:tasklet transaction-manager="jobTransactionManager">
<!-- (7) -->
<batch:chunk reader="databaseReader" writer="fileWriter"
commit-interval="200"/>
</batch:tasklet>
</batch:step>
</batch:flow>
</batch:split>
</batch:job>| Description | Sr. No. |
|---|---|
(1) |
Define a thread pool to assign to each thread for parallel processing. |
(2) |
Define steps to be executed in parallel in |
(3) |
Define |
(4) |
Step 1 of schematic diagram :Define intermediate commit method processing of chunk model. |
(5) |
Step 2 of schematic diagram :Define intermediate commit method processing of tasket model. |
(6) |
Step 3 of schematic diagram :Define batch commit method processing of tasket model. |
(7) |
Step 4 of schematic diagram :Define intermediate commit method processing for non-transactional resources of chunk model. |
|
Cases wherein processing performance deteriorates due to parallel processing
In the parallel processing, same process can be run in parallel by changing the data range, similar to multiple processing. In this case, data range is assigned by the parameters. Examples of footprints
|
Further, steps of common processing can be defined as well before and after Parallel Step process.
<batch:job id="parallelRegisterJob" job-repository="jobRepository">
<!-- (1) -->
<batch:step id="parallelRegisterJob.step.preprocess"
next="parallelRegisterJob.split">
<batch:tasklet transaction-manager="jobTransactionManager"
ref="deleteDetailTasklet" />
</batch:step>
<!--(2) -->
<batch:split id="parallelRegisterJob.split" task-executor="parallelTaskExecutor">
<batch:flow>
<batch:step id="parallelRegisterJob.step.plan">
<batch:tasklet transaction-manager="jobTransactionManager">
<batch:chunk reader="planReader" writer="planWriter"
commit-interval="1000" />
</batch:tasklet>
</batch:step>
</batch:flow>
<batch:flow>
<batch:step id="parallelRegisterJob.step.performance">
<batch:tasklet transaction-manager="jobTransactionManager">
<batch:chunk reader="performanceReader" writer="performanceWriter"
commit-interval="1000" />
</batch:tasklet>
</batch:step>
</batch:flow>
</batch:split>
</batch:job>| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1) |
Define steps to be processed as preprocessing. Specify id set in |
(2) |
Define Parallel Step. |
Partitioning Step (Multiple processing)
A method of Partitioning Step (multiple processing) is explained.
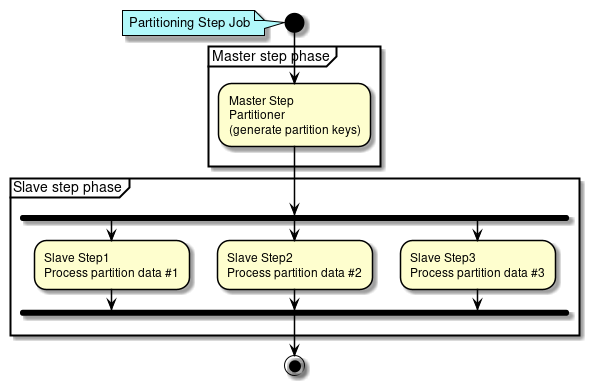
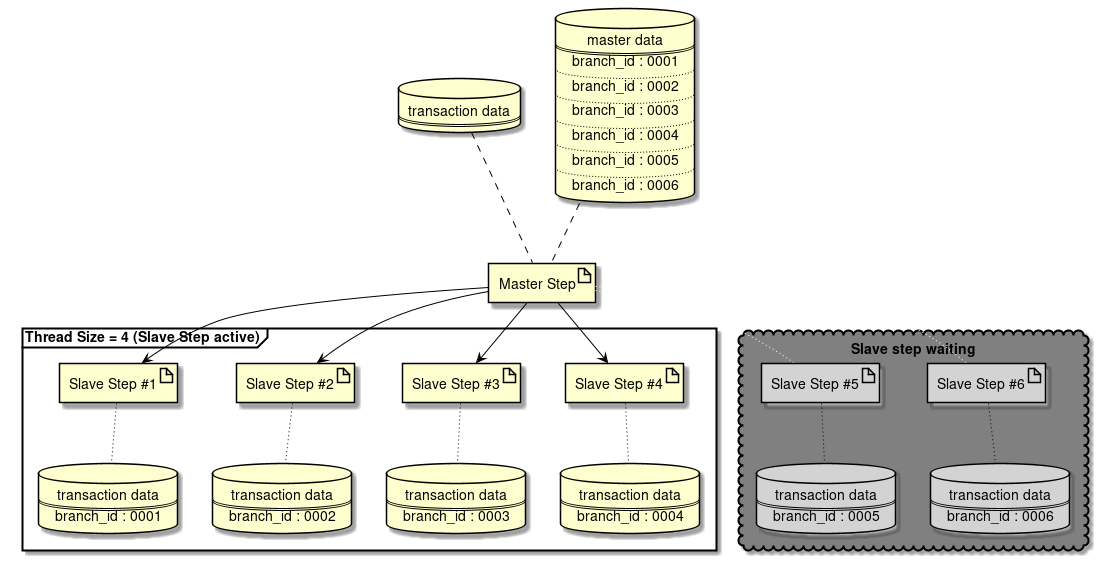
Partitioning Step is divided into processing phases of Master step and Slave step.
-
In Master step,
Partitionergenerates aParition Keyto specify data range wherein each Slave step is processed.Parition Keyis stored in the step context. -
In Slave step,
Parition Keyassigned on its own from step context is fetched and data for processing is specified using the same. Step defined for specified data for processing are executed.
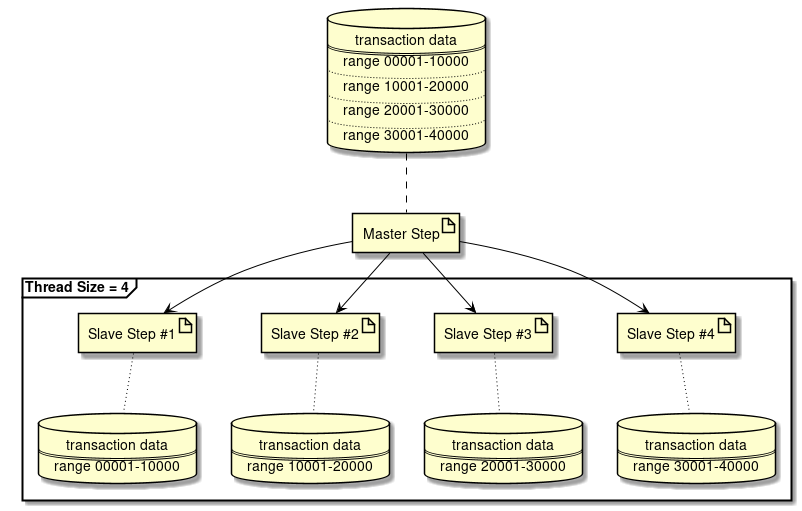
In the Partitioning Step, although it is necessary to divide the processing data, either of the variable number and fixed number are handled for the number of partitionings.
- In case of a variable number
-
Divide by department or process for each file existing in specific directory
- In case of a fixed number
-
Process data by dividing overall data in fixed numbers
In Spring Batch, fixed number is called grid-size and data partitioning range is determined so that grid-size becomes Partitioner.
In Partitioning Step, number of partitionings can be significantly higher than the thread size. In this case, multiple executions are performed using number of threads and a step is generated wherein the process is not executed until the thread becomes empty.
Use case of Partitioning Step is shown below.
| Use case | Master(Patitioner) | Slave | Number of partitionings |
|---|---|---|---|
A case wherein transaction information is divided or multiple processing is performed from master information |
DB (Master information) |
DB (Transaction information) |
Variable |
A case wherein multiple processing is performed for 1 file from a list of files |
Multiple files |
Single file |
Variable |
A case wherein a large amount of data is divided by a fixed number or multiple processing is performed A case wherein since recovery design other than re-run becomes difficult in case of a failure occurrence, it is not used the actual operation. |
Specify data range from |
DB (Transaction information) |
Fixed |
When number of partitionings are variable
A method wherein number of partitionings are made variable by Partitioning Step is explained.
Processing image is shown below.
How to implement is shown below using the processing image as an example.
<!-- (1) -->
<select id="findAll" resultType="org.terasoluna.batch.functionaltest.app.model.mst.Branch">
<![CDATA[
SELECT
branch_id AS branchId,
branch_name AS branchName,
branch_address AS branchAddrss,
branch_tel AS branchTel,
create_date AS createDate,
update_date AS updateDate
FROM
branch_mst
]]>
</select>
<!-- (2) -->
<select id="summarizeInvoice"
resultType="org.terasoluna.batch.functionaltest.app.model.performance.SalesPerformanceDetail">
<![CDATA[
SELECT
branchId, year, month, customerId, SUM(amount) AS amount
FROM (
SELECT
t2.charge_branch_id AS branchId,
date_part('year', t1.invoice_date) AS year,
date_part('month', t1.invoice_date) AS month,
t1.customer_id AS customerId,
t1.invoice_amount AS amount
FROM invoice t1
INNER JOIN customer_mst t2 ON t1.customer_id = t2.customer_id
WHERE
t2.charge_branch_id = #{branchId}
) t3
GROUP BY branchId, year, month, customerId
ORDER BY branchId ASC, year ASC, month ASC, customerId ASC
]]>
</select>
<!-- omitted -->@Component
public class BranchPartitioner implements Partitioner {
@Inject
BranchRepository branchRepository; // (3)
@Override
public Map<String, ExecutionContext> partition(int gridSize) {
Map<String, ExecutionContext> map = new HashMap<>();
List<Branch> branches = branchRepository.findAll();
int index = 0;
for (Branch branch : branches) {
ExecutionContext context = new ExecutionContext();
context.putString("branchId", branch.getBranchId()); // (4)
map.put("partition" + index, context); // (5)
index++;
}
return map;
}
}<!-- (6) -->
<task:executor id="parallelTaskExecutor"
pool-size="${thread.size}" queue-capacity="10"/>
<!-- (7) -->
<bean id="reader" class="org.mybatis.spring.batch.MyBatisCursorItemReader" scope="step"
p:queryId="org.terasoluna.batch.functionaltest.app.repository.performance.InvoiceRepository.summarizeInvoice"
p:sqlSessionFactory-ref="jobSqlSessionFactory">
<property name="parameterValues">
<map>
<!-- (8) -->
<entry key="branchId" value="#{stepExecutionContext['branchId']}" />
</map>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- omitted -->
<batch:job id="multipleInvoiceSummarizeJob" job-repository="jobRepository">
<!-- (9) -->
<batch:step id="multipleInvoiceSummarizeJob.master">
<!-- (10) -->
<batch:partition partitioner="branchPartitioner"
step="multipleInvoiceSummarizeJob.slave">
<!-- (11) -->
<batch:handler grid-size="0" task-executor="parallelTaskExecutor" />
</batch:partition>
</batch:step>
</batch:job>
<!-- (12) -->
<batch:step id="multipleInvoiceSummarizeJob.slave">
<batch:tasklet transaction-manager="jobTransactionManager">
<batch:chunk reader="reader" writer="writer" commit-interval="10"/>
</batch:tasklet>
</batch:step>| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1) |
Define a SQL wherein processing target is fetched from master data. |
(2) |
Define a SQL wherein fetched values from master data are considered as search conditions. |
(3) |
Inject defined Repository(SQLMapper). |
(4) |
Store master value processed by 1 Slave step in the step context. |
(5) |
Store each Slave in Map so that it can fetch corresponding context. |
(6) |
Define a thread pool to assign to each thread of Slave step in multiple processing. |
(7) |
Define ItemReader for fetching data using master value. |
(8) |
Fetch master value set in (4) from step context and add to search conditions. |
(9) |
Define Master step. |
(10) |
Define processing to generate partitioning conditions of data. |
(11) |
Since |
(12) |
Define Slave step. |
When multiple processing is performed for each file from the list of files, Partitioner given below offered by Spring Batch can be used.
-
org.springframework.batch.core.partition.support.MultiResourcePartitioner
How to use MultiResourcePartitioner is shown below.
<!-- (1) -->
<task:executor id="parallelTaskExecutor" pool-size="10" queue-capacity="200"/>
<!-- (2) -->
<bean id="reader"
class="org.springframework.batch.item.file.FlatFileItemReader" scope="step"
p:resource="#{stepExecutionContext['fileName']}"> <!-- (3) -->
<property name="lineMapper">
<bean class="org.springframework.batch.item.file.mapping.DefaultLineMapper"
p:fieldSetMapper-ref="invoiceFieldSetMapper">
<property name="lineTokenizer">
<bean class="org.springframework.batch.item.file.transform.DelimitedLineTokenizer"
p:names="invoiceNo,salesDate,productId,customerId,quant,price"/>
</property>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- (4) -->
<bean id="patitioner"
class="org.springframework.batch.core.partition.support.MultiResourcePartitioner"
scope="step"
p:resources="file:#{jobParameters['basedir']}/input/invoice-*.csv"/> <!-- (5) -->
<!--(6) -->
<batch:job id="inspectPartitioninglStepFileJob" job-repository="jobRepository">
<batch:step id="inspectPartitioninglStepFileJob.step.master">
<batch:partition partitioner="patitioner"
step="inspectPartitioninglStepFileJob.step.slave">
<batch:handler grid-size="0" task-executor="parallelTaskExecutor"/>
</batch:partition>
</batch:step>
</batch:job>
<!-- (7) -->
<batch:step id="inspectPartitioninglStepFileJob.step.slave">
<batch:tasklet>
<batch:chunk reader="reader" writer="writer" commit-interval="20"/>
</batch:tasklet>
</batch:step>| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1) |
Define a thread pool to be assigned to each thread of Slave step in multiple processing. |
(2) |
Define ItemReader to read a single file. |
(3) |
In |
(4) |
Define |
(5) |
Multiple files can be handled by using a pattern wherein * is used. |
(6) |
Define Master step. |
(7) |
Define Slave step. |
When number of partitionings are fixed
How to fix number of partitionings in Partitioning Step is explained.
Processing image diagram is shown below.
How to implement is shown below using the processing image as an example.
<!-- (1) -->
<select id="findByYearAndMonth"
resultType="org.terasoluna.batch.functionaltest.app.model.performance.SalesPerformanceSummary">
<![CDATA[
SELECT
branch_id AS branchId, year, month, amount
FROM
sales_performance_summary
WHERE
year = #{year} AND month = #{month}
ORDER BY
branch_id ASC
LIMIT
#{dataSize}
OFFSET
#{offset}
]]>
</select>
<!-- (2) -->
<select id="countByYearAndMonth" resultType="_int">
<![CDATA[
SELECT
count(*)
FROM
sales_performance_summary
WHERE
year = #{year} AND month = #{month}
]]>
</select>
<!-- omitted -->@Component
public class SalesDataPartitioner implements Partitioner {
@Inject
SalesSummaryRepository repository; // (3)
// omitted.
@Override
public Map<String, ExecutionContext> partition(int gridSize) {
Map<String, ExecutionContext> map = new HashMap<>();
int count = repository.countByYearAndMonth(year, month);
int dataSize = (count / gridSize) + 1; // (4)
int offset = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < gridSize; i++) {
ExecutionContext context = new ExecutionContext();
context.putInt("dataSize", dataSize); // (5)
context.putInt("offset", offset); // (6)
offset += dataSize;
map.put("partition:" + i, context); // (7)
}
return map;
}
}<!-- (8) -->
<task:executor id="parallelTaskExecutor"
pool-size="${thread.size}" queue-capacity="10"/>
<!-- (9) -->
<bean id="reader"
class="org.mybatis.spring.batch.MyBatisCursorItemReader" scope="step"
p:queryId="org.terasoluna.batch.functionaltest.ch08.parallelandmultiple.repository.SalesSummaryRepository.findByYearAndMonth"
p:sqlSessionFactory-ref="jobSqlSessionFactory">
<property name="parameterValues">
<map>
<entry key="year" value="#{new Integer(jobParameters['year'])}" />
<entry key="month" value="#{new Integer(jobParameters['month'])}" />
<!-- (10) -->
<entry key="dataSize" value="#{stepExecutionContext['dataSize']}" />
<!-- (11) -->
<entry key="offset" value="#{stepExecutionContext['offset']}" />
</map>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- omitted -->
<batch:job id="multipleCreateSalesPlanSummaryJob" job-repository="jobRepository">
<!-- (12) -->
<batch:step id="multipleCreateSalesPlanSummaryJob.master">
<!-- (13) -->
<batch:partition partitioner="salesDataPartitioner"
step="multipleCreateSalesPlanSummaryJob.slave">
<!-- (14) -->
<batch:handler grid-size="4" task-executor="parallelTaskExecutor" />
</batch:partition>
</batch:step>
</batch:job>
<!-- (15) -->
<batch:step id="multipleCreateSalesPlanSummaryJob.slave">
<batch:tasklet transaction-manager="jobTransactionManager">
<batch:chunk reader="reader" processor="addProfitsItemProcessor"
writer="writer" commit-interval="10"/>
</batch:tasklet>
</batch:step>| Sr. No. | Description |
|---|---|
(1) |
Define a pagination search (SQL narrowing down method) to fetch a specific data range. |
(2) |
Define SQL to fetch total number of records for processing. |
(3) |
Inject defined Repository(SQLMapper). |
(4) |
Calculate data records processed by one Slave step. |
(5) |
Store data records of (4) in step context. |
(6) |
Store search start position of each Slave step in step context. |
(7) |
Each Slave is stored in the Map to enable fetching of corresponding context. |
(8) |
Define a thread poolto be assigned to each thread of Slave step in multiple processing. |
(9) |
Define ItemReader for fetching data by using pagination search (SQL narrow down method). |
(10) |
Fetch data records set in (5) from step context and add to search conditions. |
(11) |
Fetch search start position set in (6) from step context and add to search conditions. |
(12) |
Define Master step. |
(13) |
Define a process which generates partitioning conditions for data. |
(14) |
Set number of partitionings (fixed number) in |
(15) |
Define Slave step. |